Key:usage
| Description |
|---|
| Describes the primary usage of railways, pipeline or waterways |
| Group: properties |
| Used on these elements |
| Documented values: 24 |
| Useful combination |
| See also |
|
| Status: de facto |
| Tools for this tag |
Railways
The key usage=* is used to identify the primary usage of a railway track. This is in principle independent of the kind of railway. It is often used with railway=rail and railway=narrow_gauge.
The distinction between main and branch line in general should be straightforward, but may be vague in certain circumstances; for example, if the branch line is very long. Some generic criteria are described in the table, below, but one should consider each case individually. Often, branch lines are described as such in the official name, however, sometimes rail is named "XYZ Main Line" even though it is more appropriately tagged usage=branch.
The distinction between the other types of usage should be more obvious.
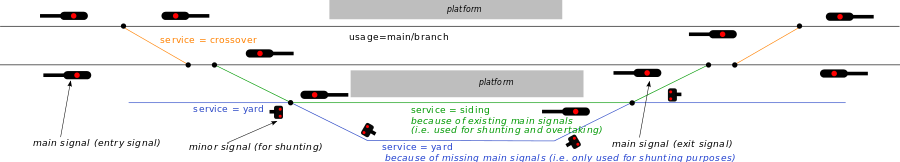
A track that is tagged with usage=main or usage=branch should not also be tagged with service=*.
Crossovers, yards, and sidings are tagged with service=* only whereas industrial, military, test and tourism railway infrastructure get both usage=* and service=*.
Inside a railway station area, use usage=main or usage=branch only for the main tracks (not for siding, yard tracks etc.). That also applies for crossover or overtaking tracks outside of the railway stations.
Values
Waterways
Pipelines
Aerialways
On aerialway=*, especially to allow for specific values of aerialway=* instead of the unspecific aerialway=goods.
Proposed usage with highways
Proposal:More road details include usage=link as a new tag for highway links that don't have a highway=*_link tag.
| This is just a proposed usage; the relevant proposal has not been voted on yet. |