Tag:man_made=pump
| Description |
|---|
| A device in charge of moving or raising the level of liquids. |
| Group: man made |
| Used on these elements |
| Useful combination |
| See also |
| Status: approved |
| Tools for this tag |
|
The tag man_made=pump is used to map a pump: a mechanical devices which is used to move liquids or raising their level.
How to map
On every pump device (not the surrounding perimeter nor building) found, place a ![]() and add the tag man_made=pump (if no other man_made=* value prevents it).
and add the tag man_made=pump (if no other man_made=* value prevents it).
Use location=* to give information about its position and pump_mechanism=* to let us know about its mechanism.
man_made=pump is only for individual pump devices. See man_made=pumping_station for pumping stations hosting pumps.
Tags used in combination
| Key | Value | Comment | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| man_made | pump | Pumps are usually mapped as |
Mandatory |
| pump_mechanism=* | <pump mechanism> | The mechanical design of the pump | Important |
| mechanical_driver=* | <driver technology> | Motion source of the pump | Important |
| mechanical_coupling=* | <coupling technology> | Mechanical equipment linking driver and the pump to transmit torque. Defaults to direct | Important |
| handle=* | <handle model> | Does a handle is available on the pump to operate manually? See below for possible values | Optional |
| location=* | <location> | The physical location of the pump, such as indoor. See below for possible values. | Optional |
| operator=* | <operator> | Name of the company that operates the pump. | Optional |
| manufacturer=* | <Manufacturing company> | Name of the company that built the pump (and possibly its driver) | Optional |
| ref=* | <reference> | Abbreviation / number of the pump. | Optional |
| pressure=* | <nominal output pressure in bar> | Nominal output pressure the pump is designed to deliver | Optional |
| flow_rate=* | <nominal output flow in m³/s> | Nominal output flow the pump can deliver. | Optional |
Although it is not usually recommended to add properties of incoming pipelines to accessory nodes, it is correct to add substance=* on pump nodes to state which substance is processed by a particular device, especially when pumps don't operates mixtures or change the state of the substance.
Pump details
Pumps are mechanical devices to move liquids and are a common component of industrial systems and water supplies. They can have many different shapes and functions. They are found in many settings, from households to heavy industries.
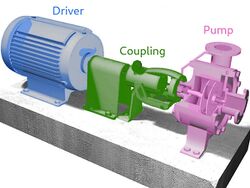
Three main components comprise a typical pump assembly: 1. driver 2. coupling and 3. pump. That is, pumps are usually powered by a driver through a coupling mechanism.
- The driver in any assembly is in charge of the conversion from the source energy to a mechanical force.
- A coupling is in charge of transmitting the power by connecting the driver and the pump mechanism.
Driver technology is not the same as pump mechanism: for instance the same reciprocating pump can be independently driven by either hand or by an electric motor.
Coupling is not the same as the driver's motion source: for instance the same "nodding donkey" coupling can independently adapt motion from electric motor, combustion engine or even manual power.
pump_mechanism=* values allow mappers to specify which kind of pump they see on ground.
Quantifiable figures and capacities may be obtained from public documentation, via nameplates or pump tags. A complete datasheet may be posted next to the pump which shows the device capabilities and mechanism.
As always, don't go inside private or restricted perimeters if you're not invited. Some pumps may not be safely accessible. Public information or aerial imagery may help to see outdoor pipeline facilities safely.
Examples
Local supply
| Photo | Location | Tagging | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Germany |
man_made=pump
|
A piston pump used to get water by manually raising and lowering the lever. The piston is located underground and move water towards the faucet and then outside of the well If the piston pump draws the water from a water well, use man_made=water_well |
 |
England | A hydraulic ram converts high flow kinetic energy into a pressure for a smaller flow, allowing it to be actually pumped. It requires no driver and external power supply so mechanical_driver=* isn't applicable here. This ram is beside an actual well head under the concrete plate behind it. |
Industrial
| Photo | Location | Tagging | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
France |
man_made=pump
|
A common radial centrifugal_pump driven by an electric motor in a drinkable water production facility |
 |
The Netherlands |
man_made=pump
|
A common radial centrifugal pump driven by an electric motor probably used for irrigation or water reservoir feeding |
 |
- |
man_made=pump
|
An inline centrifugal pump driven by an electric motor. Centrifugal pumps can sometimes find inline, with less axial efforts than radial ones. |
 |
Austria |
man_made=pump
|
A common progressive cavity pump driven by an electric motor used for oil pumping in heavy machinery. See below for running principle. |
 |
International sea |
man_made=pump
|
A common diaphragm pump driven by a pneumatic cylinder, installed here on a boat deck (so please don't map it in place). This example shows the diaphragm shape that can't be confused with any other mechanism. See below for running principle. |
 |
France |
man_made=pump
|
This example focus on coupling an electric motor to centrifugal pump with a belt. Both pump and motor are behind the blue casing. |
 |
- |
man_made=pump
|
Pumps figure plates can help to define OSM tags values. Here is how this example is evaluated: |
 |
USA |
man_made=pump
|
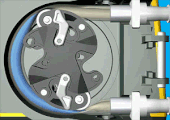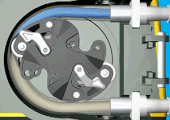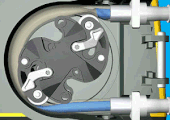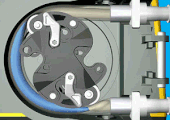
A peristaltic pump involved in a chemical process with potentially dangerous fluids. The box between the electric motor and the pump is a reducer to slow the rotation speed and increase the torque as to move the fluid in the pipe. |
 |
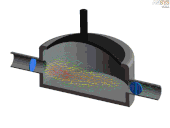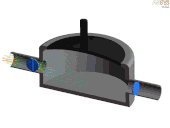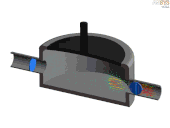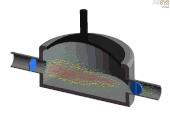
Germany | A rotary vane pump mechanism only where driver and coupling remain undetermined. See below for running principle. |
Hydropower
| Photo | Location | Tagging | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Switzerland |
man_made=pump
|
Hydropower generation sometimes involves pump for large scale water storage. Some power plants have pumps separated from turbines like in Veytaux, Switzerland where a 600 tons multi-stage centrifugal pump is located below a Pelton turbine, linked by a direct coupling (see this chart). The pump is driven by the generator used as an electric motor with electricity coming from transmission grid. When the pump is running, the Pelton turbine runs empty without water. |
See also
- man_made=pumping_station – A facility including pumps and equipment for pumping fluids from one place to another
- IEEE Engineering 360 portal about pumps
- LEWA pumps navigator to help designing a pump solution based on factual criteria. (Disclaim: this link is not here for commercial reasons and this proposal isn't supported by the company by any means)