Tag:highway=motorway_link
| Description |
|---|
| The link roads (sliproads / ramps) leading to and from a motorway. |
| Rendering in OSM Carto |

|
| Group: highways |
| Used on these elements |
| Requires |
|
| Implies |
| Useful combination |
|
| See also |
| Status: de facto |
| Tools for this tag |
|
Use highway=motorway_link for link roads (sliproads / ramps) leading to and from a highway=motorway. These normally have motorway restrictions. These are commonly referred to as On-ramps and Off-Ramps in American English.
How to map
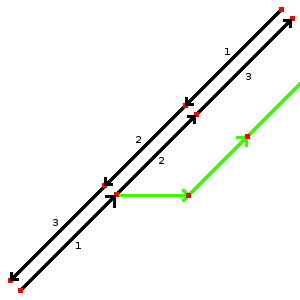
Mapping a motorway link is quite easy. In the first example (image 1) you can see a dual carriage motorway where another way (green) branches off. This green way should be tagged with highway=motorway_link and oneway=yes. Place the node where the green way branches off at the exit of the motorway as shown in image 2.
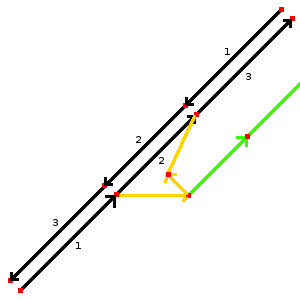
The second example (image 3) shows a more difficult junction. In this example you can leave the highway and enter it. For this create 2 different ways (orange) and tag them separately with highway=motorway_link and oneway=yes. Be sure to check the direction of the arrows. If there is no physical seperation (e.g. grass) in a part of the motorway_link you need the green way. In this example that green way can be tagged with highway=motorway_link and oneway=no.
| Tag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ref=* | Reference number, if one exists (i.e. a route takes an exit from a motorway). | 16 |
| oneway=* | 'yes' to mean it is one way, 'no' to mean it is two way. See #Tagging oneway notes | yes |
| lanes=* | Number of lanes. | 1 |
| maxspeed=* | The maximum speed which is allowed (in km/h). | 100 |
| destination=* | Name of town for the direction of the motorway_link. Use the name of the city written on the sign which belongs to the motorway_link. | London |
Tagging oneway
Most motorway_link roads will be one way, and should be tagged oneway=yes. Any unusual motorway link road which is two-way should be explicitly tagged oneway=no. Note that this is different to the way we treat other highway classifications, because motorway link roads are so often one way. Explicit tagging (either way) can be important, since some tools interpret motorway link roads as implicitly oneway=yes unless tagged oneway=no.
Motorway junction identification
At motorway exits, add the junction number or name.
- highway=motorway_junction Indicates an exit to an interchange (motorway to other motorway) or an exit to surface streets (motorway to non-motorway). Tags ref=* and name=* should be set to give the exit number (e.g., US, UK, Spain) or the exit name (e.g., France, Germany, Italy). The tags belong on the node shared by the motorway_link exit way and the through carriageway/through lanes of the motorway/freeway itself. Please note that ref=* and name=* are designed to store the reference and the name of the junction itself, not for the destination of the connected link nor the reference of the road the junction gives access to; for such data, use destination:ref=* and destination=* on the link starting at the junction.
Other situations

Parallel carriageways
A parallel motorway carriageway (US: parallel lanes) such as a collector/distributor road or physically separated HOV lanes / reversible lanes should be tagged as motorway_link. If the major road is classed as trunk or principal, then that class of _link shall be used instead.
Link roads between different highways types
In most countries, if a road leads from a motorway to a non-motorway, only the portion that solely carries traffic to or from the motorway should be tagged as motorway_link. Any other roads used to connect the motorway to a non-motorway, which can also be used by non-motorway traffic, should be tagged as something less than motorway_link, usually the *_link of the non-motorway.
In the United States, this is not applicable. The consensus and position of the DWG in the United States is that motorway_link is based on physical characteristics alone, and that they end where the ramp meets the surface street regardless of direction or use by other transportation modes.
Motorway service areas
Besides its use for on/off ramps, motorway_link is also used for the slip roads/ramps into and out of motorway service areas/rest areas. In this case the motorway_link should go from the motorway towards the services as far as motorway regulations (for example no pedestrians) apply. In the UK, this is indicated by a sign. Similarly the exit road from the services should be a motorway_link from the point where motorway regulations commence.
In the US, there are some motorway_links like this for which motorway regulations technically end somewhere before the end of a ramp, and may have sidewalks or other pedestrian features. These are still to be tagged as motorway_link all the way up to where the ramp physically ends at an at-grade intersection.
See also
- highway=motorway junction
- Link (highway)
- Lane_assist - best practices for lane assistant using turn=* and destination=*
- Talk:Lane assist/Examples/Motorway exit#Setting the split (location of the motorway junction node)
- Proposed_features/Motorway_link_obligatory_oneway
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||