Power networks

This project aims to map and document all power networks on the planet : from the largest cross-border transmission grids to small rural microgrids.
This includes the physical infrastructure that makes electricity generation, transmission, and distribution possible, such as power lines and cables, tower and poles, power plants and substations.
Power infrastructure is critical for modern life and very useful for navigation, particularly for overhead lines.
Yet, it is still under-mapped in many regions. By contributing to this project, you help build a global, open dataset that supports energy access, climate resilience, disaster response, and infrastructure planning.
What’s not included :
While oil and gas infrastructure is essential for energy systems, it is not mapped under the power=* unless it is directly part of electricity generation. For pipelines and related infrastructure, refer to the dedicated Oil and Gas Infrastructure page.
Tips :
If you are a power user, join the category:power user.
There is an IRC channel for discussing power networks and other infrastructure: irc.oftc.net #osm-infrastructure.
Electric power
Power network
Stages of electric grids

Electric power networks are structured in three main stages. Understanding these helps mappers choose the right tags and interpret the role of infrastructures.
Generation
Electricity generation is the first stage in the electric grid and it is where electricity is produced from various energy sources (fossil fuels, hydro, solar, wind, nuclear, biomass, ...). Facilities are mapped with power=plant and/or power=generator. For more information, please refer to the dedicated page Power generation.
Transmission
Power transmission is electricity being transmitted over long distanced at high voltage (100 kV and more), in order to reduce lossess. Transmission networks connect power plants to major substations, major industry facilities, or between regions.
Distribution
Electric power distribution is the final stage where electricity is delivered to consumers, at mid- and low voltages.
Physical components of an electric grid
Power plants
A facility that generates electricity from different sources. Map as an ![]() ; tag with
; tag with power=plant and describe the technology using generator:source=* and generator:type=*. More information here : Electricity generation.
Substations
A site where voltage is transformed and electricity is routed between lines. Map as an ![]() and tag with
and tag with power=substation, and use substation=* to define its role (e.g. transmission, distribution). More information here : Substations.
Lines

An overhead line carrying electricity over long distances and used for generation and transmission. Sometimes visible in satellite imagery, they are always supported at regular intervals by either towers or poles. Map as an ![]() and tag with at minimum
and tag with at minimum power=line. More information here : Power lines and Classification of power lines
Minor lines
A mid- and low voltage overhead line used in distribution. Map as an ![]() and with at minimum
and with at minimum power=minor_line. More information here : Power lines and Classification of power lines
Towers
A large metal structure that supports high-voltage overhead lines. Built on-site and varying in shape, it is often visible in satellite imagery by its star-shaped or π-shaped footprint. Map as a ![]() and tag with
and tag with power=tower. Map as with power=tower.
Poles
A smaller structure for supporting minor lines or cables. Typically made of wood or metal, with a simple T-shaped crossbar. Map as a ![]() and tag with
and tag with power=pole.
Cables
An underground or underwater line used instead of overhead transmission. Not visible from satellite imagery; it should only be mapped if technical knowledge and sources are available. Map as an ![]() and tag with at minimum
and tag with at minimum power=cable.
Types of electric grids
Electric grids vary by scale and function. These distinctions can help guide tagging and context.
Supergrids

Large-scale, cross-border networks using high-capacity transmission (often HVDC). Lines should be tagged with power=line with high voltage=*.
Wide area grids
National or regional grid connecting generators, substations, and consumers. Most power=* infrastructure belongs to this category.
Microgrids
Small local power networks (e.g. islands, campuses, regions with no transmission grid) that may operate independently. Lines should be tagged with mid- and low- voltages.
Tags
The full list of power-related tags can be found on the power=* page.
Proposals
Refer to the page category on Proposals for power networks.
Mapping guidelines
- Power networks/Guidelines
- Power networks/Guidelines/Power lines
- Power networks/Guidelines/Substations
- Power generation/Guidelines/Hydropower
- Power generation/Guidelines/Solar plants
- Power networks/Guidelines/Interconnector
Rendering
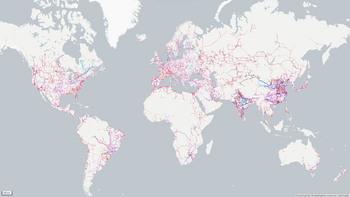
Open Infrastructure Map renders electricity, telecommunications, water, petroleum, and microwave communications infrastructure, also features a similar rendering of power lines in one of its overlays, Names of substations and their highest voltage, and power plants are also indicated.
Another visualization can be seen at Flosm.de.
MapCSS style
A mapCSS stylesheet is available for josm.
Local projects
Local projects intend to document practices, knowledge and mapping guidelines relevant for a particular area in the world only. Feel free to create a dedicated one for your region if missing. Such page should only cover particular area (like countries or region) but not a given infrastructure or facility for sake of consistency. To create a new page, you may use the dedicated template, see : Power networks/Guidelines/Country page.
- Power networks/China (x)
- Power networks/Great Britain (x)
- Power networks/Indonesia (translation in Indonesian)
- Power networks/Malaysia (translation in Malay)
- Power networks/Netherlands (x)
Local projects in Africa
![]() Algeria -
Algeria - ![]() Angola -
Angola - ![]() Benin -
Benin - ![]() Botswana -
Botswana - ![]() Burkina Faso -
Burkina Faso - ![]() Burundi -
Burundi - ![]() Cameroon -
Cameroon - ![]() Cape Verde -
Cape Verde - ![]() Central African Republic -
Central African Republic - ![]() Chad -
Chad - ![]() Comoros -
Comoros - ![]() Democratic Republic of the Congo -
Democratic Republic of the Congo - ![]() Djibouti -
Djibouti - ![]() Egypt -
Egypt - ![]() Equatorial Guinea -
Equatorial Guinea - ![]() Eritrea -
Eritrea - ![]() Eswatini -
Eswatini - ![]() Ethiopia -
Ethiopia - ![]() Gabon -
Gabon - ![]() Ghana -
Ghana - ![]() Guinea -
Guinea - ![]() Guinea-Bissau -
Guinea-Bissau - ![]() Ivory Coast -
Ivory Coast - ![]() Kenya -
Kenya - ![]() Lesotho -
Lesotho - ![]() Liberia -
Liberia - ![]() Libya -
Libya - ![]() Madagascar -
Madagascar - ![]() Malawi -
Malawi - ![]() Mali -
Mali - ![]() Mauritania -
Mauritania - ![]() Mauritius -
Mauritius - ![]() Morocco -
Morocco - ![]() Mozambique -
Mozambique - ![]() Namibia -
Namibia - ![]() Niger -
Niger - ![]() Nigeria -
Nigeria - ![]() Republic of the Congo -
Republic of the Congo - ![]() Rwanda -
Rwanda - ![]() Senegal -
Senegal - ![]() Seychelles -
Seychelles - ![]() Sierra Leone -
Sierra Leone - ![]() Somalia -
Somalia - ![]() South Africa -
South Africa - ![]() South Sudan -
South Sudan - ![]() Sudan -
Sudan - ![]() São Tomé and Príncipe -
São Tomé and Príncipe - ![]() Tanzania -
Tanzania - ![]() The Gambia -
The Gambia - ![]() Togo -
Togo - ![]() Tunisia -
Tunisia - ![]() Uganda -
Uganda - ![]() Zambia -
Zambia - ![]() Zimbabwe -
Zimbabwe -
Local projects in Asia
![]() Afghanistan -
Afghanistan - ![]() Armenia -
Armenia - ![]() Azerbaijan -
Azerbaijan - ![]() Bahrain -
Bahrain - ![]() Bangladesh -
Bangladesh - ![]() Bhutan -
Bhutan - ![]() Brunei -
Brunei - ![]() Cambodia -
Cambodia - ![]() India -
India - ![]() Indonesia -
Indonesia - ![]() Iran -
Iran - ![]() Iraq -
Iraq - ![]() Israel -
Israel - ![]() Japan -
Japan - ![]() Jordan -
Jordan - ![]() Kazakhstan -
Kazakhstan - ![]() Kuwait -
Kuwait - ![]() Kyrgyzstan -
Kyrgyzstan - ![]() Laos -
Laos - ![]() Lebanon -
Lebanon - ![]() Malaysia -
Malaysia - ![]() Maldives -
Maldives - ![]() Mongolia -
Mongolia - ![]() Myanmar -
Myanmar - ![]() Nepal -
Nepal - ![]() North Korea -
North Korea - ![]() Oman -
Oman - ![]() Pakistan -
Pakistan - ![]() People's Republic of China -
People's Republic of China - ![]() Philippines -
Philippines - ![]() Qatar -
Qatar - ![]() Saudi Arabia -
Saudi Arabia - ![]() Singapore -
Singapore - ![]() South Korea -
South Korea - ![]() Sri Lanka -
Sri Lanka - ![]() State of Palestine -
State of Palestine - ![]() Syria -
Syria - ![]() Taiwan -
Taiwan - ![]() Tajikistan -
Tajikistan - ![]() Thailand -
Thailand - ![]() Timor-Leste -
Timor-Leste - ![]() Turkey -
Turkey - ![]() Turkmenistan -
Turkmenistan - ![]() United Arab Emirates -
United Arab Emirates - ![]() Uzbekistan -
Uzbekistan - ![]() Vietnam -
Vietnam - ![]() Yemen -
Yemen -
Local projects in Europe
![]() Albania -
Albania - ![]() Andorra -
Andorra - ![]() Austria -
Austria - ![]() Belarus -
Belarus - ![]() Belgium -
Belgium - ![]() Bosnia and Herzegovina -
Bosnia and Herzegovina - ![]() Bulgaria -
Bulgaria - ![]() Croatia -
Croatia - ![]() Cyprus -
Cyprus - ![]() Czech Republic -
Czech Republic - ![]() Estonia -
Estonia - ![]() Finland -
Finland - ![]() France -
France - ![]() Georgia -
Georgia - ![]() Germany -
Germany - ![]() Greece -
Greece - ![]() Hungary -
Hungary - ![]() Iceland -
Iceland - ![]() Ireland -
Ireland - ![]() Italy -
Italy - ![]() Kingdom of Denmark -
Kingdom of Denmark - ![]() Kingdom of the Netherlands -
Kingdom of the Netherlands - ![]() Latvia -
Latvia - ![]() Liechtenstein -
Liechtenstein - ![]() Lithuania -
Lithuania - ![]() Luxembourg -
Luxembourg - ![]() Malta -
Malta - ![]() Moldova -
Moldova - ![]() Monaco -
Monaco - ![]() Montenegro -
Montenegro - ![]() North Macedonia -
North Macedonia - ![]() Norway -
Norway - ![]() Poland -
Poland - ![]() Portugal -
Portugal - ![]() Romania -
Romania - ![]() Russia -
Russia - ![]() San Marino -
San Marino - ![]() Serbia -
Serbia - ![]() Slovakia -
Slovakia - ![]() Slovenia -
Slovenia - ![]() Spain -
Spain - ![]() Sweden -
Sweden - ![]() Switzerland -
Switzerland - ![]() Ukraine -
Ukraine - ![]() United Kingdom -
United Kingdom - ![]() Vatican City -
Vatican City -
Local projects in Oceania
![]() Australia -
Australia - ![]() Federated States of Micronesia -
Federated States of Micronesia - ![]() Fiji -
Fiji - ![]() Kiribati -
Kiribati - ![]() Marshall Islands -
Marshall Islands - ![]() Nauru -
Nauru - ![]() New Zealand -
New Zealand - ![]() Palau -
Palau - ![]() Papua New Guinea -
Papua New Guinea - ![]() Samoa -
Samoa - ![]() Solomon Islands -
Solomon Islands - ![]() Tonga -
Tonga - ![]() Tuvalu -
Tuvalu - ![]() Vanuatu -
Vanuatu -
Local projects in North America
![]() Antigua and Barbuda -
Antigua and Barbuda - ![]() Barbados -
Barbados - ![]() Belize -
Belize - ![]() Canada -
Canada - ![]() Costa Rica -
Costa Rica - ![]() Cuba -
Cuba - ![]() Dominica -
Dominica - ![]() Dominican Republic -
Dominican Republic - ![]() El Salvador -
El Salvador - ![]() Grenada -
Grenada - ![]() Guatemala -
Guatemala - ![]() Haiti -
Haiti - ![]() Honduras -
Honduras - ![]() Jamaica -
Jamaica - ![]() Mexico -
Mexico - ![]() Nicaragua -
Nicaragua - ![]() Saint Kitts and Nevis -
Saint Kitts and Nevis - ![]() Saint Lucia -
Saint Lucia - ![]() Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines - ![]() The Bahamas -
The Bahamas - ![]() Trinidad and Tobago -
Trinidad and Tobago - ![]() United States -
United States -
Local projects in South America
![]() Argentina -
Argentina - ![]() Bolivia -
Bolivia - ![]() Brazil -
Brazil - ![]() Chile -
Chile - ![]() Colombia -
Colombia - ![]() Ecuador -
Ecuador - ![]() Guyana -
Guyana - ![]() Panama -
Panama - ![]() Paraguay -
Paraguay - ![]() Peru -
Peru - ![]() Suriname -
Suriname - ![]() Uruguay -
Uruguay - ![]() Venezuela -
Venezuela -
Quality Assurance
See : Power_networks/Quality_Assurance
Organized editing activities
For more information, please refer to the dedicated Organised Editing/Activities page.
Research and scientific articles
- Xiong, B., Fioriti, D., Neumann, F., Riepin, I., Brown, T., 2024. Modelling the High-Voltage Grid Using Open Data for Europe and Beyond. ArXiv preprint. URL.
- Oughton, E. J., Peters, E. A., Bor, D., Rivera, N., Gaunt, C. T., & Weigel, R., 2024. A reproducible method for mapping electricity transmission infrastructure for space weather risk assessment. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.17685
- Wang, Z., Majumdar, A., & Rajagopal, R., 2023. Geospatial mapping of distribution grid with machine learning and publicly-accessible multi-modal data. Nature Communications, 14, 5006. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39647-3
- Arderne, C., Zorn, C., Nicolas, C. et al, 2020. Predictive mapping of the global power system using open data. Sci Data 7, 19.
- Arderne, C., Zorn, C., Nicolas, C. et al., 2020. Predictive mapping of the global power system using open data. Sci Data, 7(19). DOI.
- Wided, M., Muller, U.P., Scharf, M., Matke, C., Kleinhans, D., 2017. Open Data in Power Grid Modelling: New Approaches Towards Transparent Grid Models. Energy Reports, 3, pp. 14-21, DOI.
- OpenGridMap Initiative, Technical University of Munchen. More information and sources here.
- OpenGridMap: An Open Platform for Inferring Power Grids with Crowdsourced Data, José Rivera , Christoph Goebel, David Sardari, Hans-Arno Jacobsen, Energy Informatics, Volume 9424 of the series Lecture Notes in Computer Science pp 179-191, 06 January 2016.
- OpenGridMap: towards automatic power grid simulation model generation from crowdsourced data Rivera, J., Leimhofer, J. & Jacobsen, HA. Comput Sci Res Dev (2016). doi:10.1007/s00450-016-0317-4
OSM in energy projects worldwide
See also
Note on oil and gas power
Oil and gas infrastructure is not tagged with power=* unless it directly relates to electricity generation.
If oil or gas is used as a fuel in a power plant, the recommended tags power=plant and generator:source=oil or generator:source=gas.
Pipelines, wells, refineries, and storage tanks are part of the petroleum or gas industries, not the electric power network.
For detailed information on this subject, please refer to the dedicated Oil and Gas Infrastructure page.
Open Infrastructure Map shows man_made=pipeline and substance=* on ways and areas.
Pipelines
man_made=pipeline"Here is a pipeline"location=*underground|underwater|overground (optional)substance=valueThis can be <water|oil|gas|sewage|any substance> (optional)operator=name<name of the company operating the pipeline> (optional)
- Germany: Gasnetzkarte
| Abkürzung | Name der Pipeline | Marker von - Marker bis | osm data | Kommentar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWO | Nord-West-Oelleitung | 19,34,36,37 | 30780560 |
|
| RRB | [Rohrleitung Rostock Böhlen] | 690-692 | 35103657 |
Quellen: [1] |
Substations
See pipeline=substation for any facility involving pipelines for inspection, compression or storage
Proposals
- Pipeline extension proposal.