Unite Maps Initiative/UN Mappers/OSM Features in Democratic Republic of the Congo
In this page you can find the editing guidelines used in the Unite Maps initiative to add topographic data in Democratic Republic of the Congo, to help UN peacekeeping operations brought by MONUSCO.
General Instructions
For this Mission, the important features are:
If you are new to OpenStreetMap editing, you can start from here. For any other feature not covered in this guide, please refer to the general OSM Feature list always checking the local community editing guidelines, if any, in that country. In Democratic Republic of the Congo, OSM editing is managed by OSM RDC.
Highways
Highway extraction is an important task for the production of topographic maps. Highways must be mapped with correct geometry and tags. Among those, hierarchy attributes highway=* and surface surface=* are the most important.
The classification of an highway depends not only on its width but more importantly from the role that road is playing within the overall road network. Find more in the general editing guideline.
Highways for those areas MUST be mapped accordingly to the Highway Tag Africa guideline. You can find a brief summary below.
The most frequent tags for road hierarchy in this area are:
While for the surface type, generally use:
Highways classification
When mapping highways, the clue of classification is mainly the social and economic role of the way, that means it's importance as communication axe.
| Tag (key, value) | Type | Description | Satellite image | Field image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
highway=primary
|
Primary Road | Major transportation route between and into major cities within a country.
Engineered alignment. |
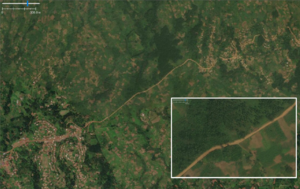 |
 |
highway=secondary
|
Secondary Road | Major transportation route between cities and large towns.
Collector function in urban areas. It starts from a |
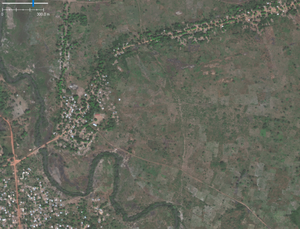 |
 |
highway=tertiary
|
Tertiary Road | Major transportation route between towns and larger villages.
Collector function in urban areas. It starts from a |
 |
 |
highway=track
|
Track Road | Access route from dwellings to agricultural and forestry areas.
No connection function between settlements. |
 |
 |
highway=path
|
Path | Travel route between small dwellings, water sources or for livestock movement.
May be the primary access route for isolated settlements. Can be used instead of Steep grades, narrow width, irregular alignment, obstacles, boulders, stream crossings, and seasonal use. |
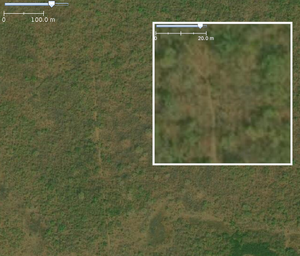 |
|
highway=unclassified
|
Unclassified Road | Minor roads that allow travel and commerce from paths and residential roads between villages and dwellings.
Connection function between settlements. While generally not residential, there can be houses along the road. |
 |
 |
highway=residential
|
Residential Road | In urban areas or rural villages, roads which serve as an access to housing, without function of connecting settlements. Often lined with housing.
This tag is used only in urban areas and only on roads which serve no other purpose than residential. |
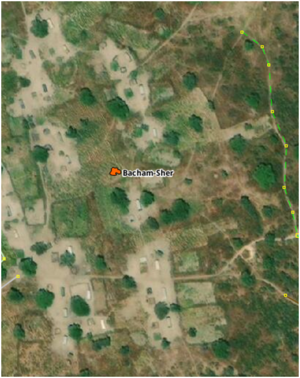 |
 |
highway=service +
|
Alley | Informal roads, not inserted in the urban grid. Not always connecting main communication axes. May be within households or compounds.
This tag is used only in urban areas and only on roads which serve no other purpose than residential. |
 |
Waterways
Waterways has to be mapped in a network-like structure as highways. Similarly to roads, hierarchy of waterways is important and defined by waterway=*.
Big rivers may be mapped as relations (for more, see Relation:waterway. By the way, for our mapping activities, mapping them as lines is more than sufficient.
Many rivers in this area may be intermittent or seasonal, meaning that the water is not present on the ground all-year long. If a river is seasonal, the right tagging is the combination of both intermittent=yes + seasonal=yes.
The most frequent tags for waterways in this area are:
While to target seasonality, where needed, generally use:
For further information about the mapping of rivers, you can visit the dedicated river mapping guide.
Waterways classification
| Tag (key, value) | Type | Description | Satellite image |
|---|---|---|---|
waterway=river
|
River | Major waterway, collecting and distributing water through canals and streams.
Width: >10 meters. |
 |
natural=water + water=river
|
Riverbank | If a riverbank is visible from satellite imagery, it has to be mapped as polygon. A line for the waterway=river must be drawn inside the riverbank as shown in photo.
If the river is seasonal or intermittent, please add the same tags to the riverbank. If a river has a name, apply the name to the line and not to the riverbank. It can be used together with Width: >10 meters. |
 |
waterway=stream
|
Stream | Minor waterway, connected to a river.
Width: <10 meters. Most of the times ‘You could jump over it’. |
 |
Landcover
Landcover represents the vegetation or the soil composition visible from satellite imagery, without any relationship to their usage.
Landcover can be mapped as:
- Polygon, if it doesn’t have any different landcover class inside it. The rule here is 'One_feature,_one_OSM_element'. As for that, polygons mapped as landcover must not intersect or overlap landuse polygons.
- Multipolygon relation, if it does have other landcover classes completely falling inside the outer polygon. In this case, the outer polygon may be composed by many separate lines. The class of the outer landcover is assigned to the relation and not to the outer ways.
The most common landcover classes in this area are:
Landcover classification
| Tag (key, value) | Type | Description | Satellite image |
|---|---|---|---|
natural=wood
|
Wood | Tree-covered area (a 'forest' or 'wood').
This area is not maintened with human intervention, differently from |
 |
natural=wetland
|
Wetland | A natural area subject to inundation or with waterlogged ground.
It can be further specified with |
 |
natural=grassland
|
Grassland | Areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous (non-woody) plants, excluding cultivated areas and wetlands. | 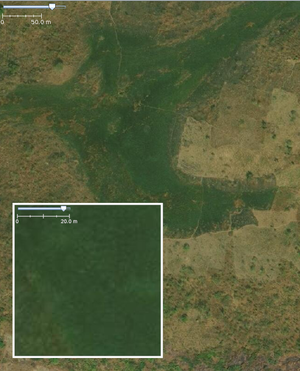 |
natural=scrub
|
Scrub | Uncultivated land covered with shrubs, bushes or stunted trees. |  |
natural=bare_rock
|
Rock | An area with sparse or no vegetation, so that the bedrock becomes visible. |  |
natural=shingle
|
Shingle | Shingle is an accumulation of rounded rock fragments, usually pebbles and gravel, but sometimes larger, deposited and shaped by movement of water. It is used in two contexts: shingle beach and river shingle.
In contrast to It can be used together with |
 |
natural=water
|
Natural water | Any body of water, from natural such as a lake or pond to artificial like moat or canal.
You can further the kind of water body with |
 |
Landuse
Landuse represents the specific use of soil for human activities.
Landuse can be mapped as:
- Polygon, if it doesn’t have any different landuse class inside it. The rule here is 'One_feature,_one_OSM_element'. As for that, polygons mapped as landuse must not intersect or overlap landcover polygons.
- Multipolygon relation, if it does have other landuse classes completely falling inside the outer polygon. In this case, the outer polygon may be composed by many separate lines. The class of the outer landuse is assigned to the relation and not to the outer ways.
The most common landuse classes in this area are:
Landuse classification
| Tag (key, value) | Type | Description | Satellite image |
|---|---|---|---|
landuse=farmland
|
Farmland | An area of farmland used for tillage (cereals, vegetables, oil plants but also flowers). |  |
landuse=orchard
|
Orchard | This tag is used to mark intentional planting of trees or shrubs maintained for food production, including orchards and similar plantations. Orchards usually comprise fruit or nut-producing trees grown for commercial production.
This tag is also used for tropical plantations of perennial plants used to produce food and beverages, including tea, coffee, banana and oil palm plantations. The tag also applies to fruit and berry gardens, generally synonymous with an orchard, but on a smaller scale and may emphasize berry shrubs in preference to fruit trees. The tag is not recommended for a garden producing vegetables under some fruit trees when the vegetable production is the main use and the trees are too scarce. The soil of an orchard can be covered with grass or be naked, but generally worked yearly. The production is gathered. You can also specify the crop type with |
 |
landuse=residential
|
Residential area | An area of land dedicated to, or having predominantly residential buildings such as houses or apartment buildings.
This landuse tag is mostly used for larger areas and not at parcel granularity. |
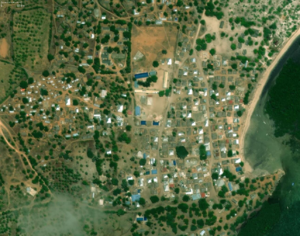 |
landuse=industrial
|
Industrial area | This tag delineates areas of land used for industrial purposes. Industrial land may include buildings like workshops, factories or warehouses and their associated infrastructure (car parks, service roads, yards and so-on).
Occasionally several industrial tenants may occupy one property in which case the property itself may be known as an industrial park. |
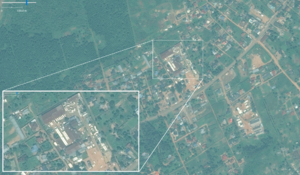 |
landuse=quarry
|
Quarry or
Mining activity |
A quarry is an area of land used for surface extraction (open-pit mining) of mineral or organic resources like rocks, gravel, sand, soil, clay, ore, coal or peat. |  |
landuse=military
|
Military area | Area used for military purposes
In some countries it is prohibited to map military areas, or legal status of these actions is unclear - but it is not against OSM rules to map those areas. |
 |
landuse=military +
(e.g. YYYY-MM-DD) |
Military post | Buildings where soldiers live and work.
The settlements very often are temporary, so also the date should be added. You may want to explore the usage of OSM time formatting and lifecycle prefixes. It can be further specified with In some countries it is prohibited to map military areas, or legal status of these actions is unclear - but it is not against OSM rules to map those areas. |
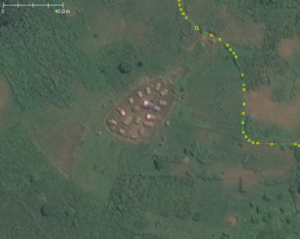 |
aeroway=aerodrome
|
Airport | The extent of an airport land (often co-incident with a barrier of some kind). | 
|
Point of interest and other features
A point of interest (POI) is a term used in cartography for the choice to represent a particular feature using an icon that occupies a particular point.
- A POI does not necessarily have to be stored as a point in a geodatabase (see #In OSM for details particular to us); it merely is represented as a point in the user interface (for example, in the standard tile layer).
- Do not take the 'of interest' part too literally; a feature might be quite ordinary, such as the postboxes mentioned above, and only in the context of the map user wanting to mail something does it become "interesting". As such, POIs are often
amenity=*.
Some examples of POIs in this area are:
POIs classification
| Tag (key, value) | Type | Description | Satellite image |
|---|---|---|---|
man_made=tower +
|
Communications tower | A tower is a free-standing structure which is higher than it is wide. It can stand alone or as a part of a bigger building.
A communication tower is no bigger than 100 m and has not the transmission facilities in the tower dome. |
 |
man_made=water_tower
|
Water tower | A water tower is a structure which contains a water tank at an altitude. | |
amenity=place_of_worship +
|
Religious site | All places of worship, independently of the religion or denomination, get the tag amenity=place_of_worship.
This covers mosques, churches, cathedrals, synagogues, temples, etc. |